First Wave: 1990s
Prescription Opioids
Rise in opioid overdose deaths prescribed by doctors
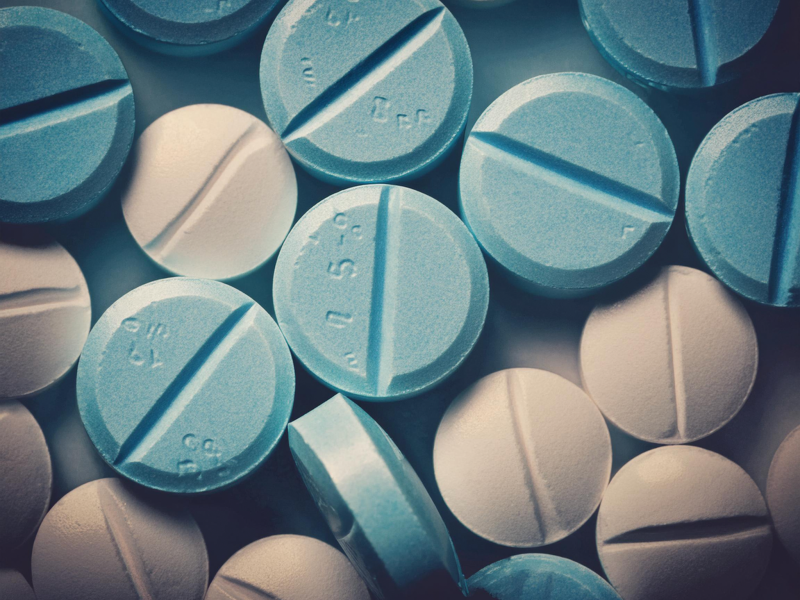
Fentanyl, a synthetic opioid, has dramatically reshaped the landscape of drug abuse in the United States, marking a lethal phase in the ongoing opioid crisis. Originally developed for pain management, its potent properties have made it a common adulterant in street drugs, contributing to a significant rise in poisoning and overdose deaths.
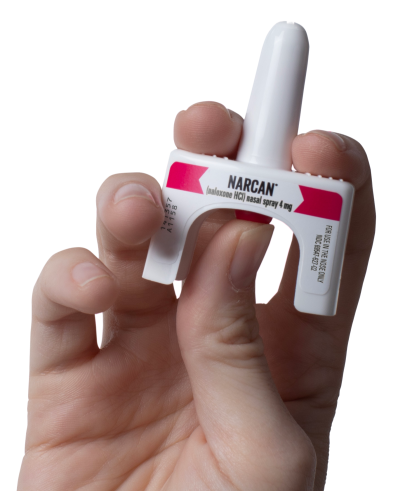
Below, are informational segments about opioids, the escalation of the crisis through its three waves, and the alarming prevalence of illicit fentanyl. We’ll explore how opioids can lead to poisoning and overdose, the symptoms to watch for, and effective harm reduction strategies, including the use of NARCAN (Naloxone) to reverse overdoses.
Our goal is to equip you with knowledge and tools to combat this crisis effectively.
Opioids are a class of drugs that include both legal prescription pain relievers and illegal substances. Derived originally from the opium poppy plant, they are used medically to treat pain but also have high potential for dependency and abuse. This has led to a complex opioid crisis, unfolding in three distinct waves. We are currently in the third wave dominated by synthetic opioids, particularly fentanyl, which is exponentially more potent and has led to a dramatic increase in overdose deaths. Each wave reflects a shift in the opioid landscape, compounding the urgency to address the crisis effectively.
Rise in opioid overdose deaths prescribed by doctors

Illegal heroin usage becomes the primary cause of overdose deaths

Including illicitly made fentanyl, becomes the number one cause of overdose deaths
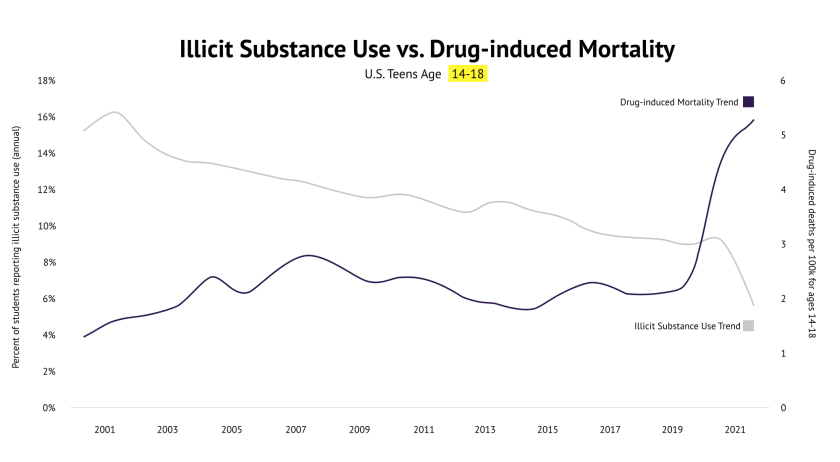
And is specifically connected to over 71,000 of the near 81,000 opioid overdose deaths in 2021. This is more than car accidents (22,442), suicide (21,678), COVID (21,335), and cancer (17,114).
The lethal dose of fentanyl is equivalent to as low as 2mg or about 3-4 grains of sand, comparable to what could fit on a pencil.


It is extremely difficult to tell the difference between real and fake fentanyl prescriptions.
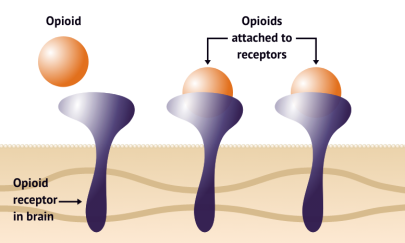
Opioids disrupt the body’s natural drive to breath cause someone to lose oxygen to the brain and potentially die within minutes. An opioid overdose happens when too much of the drug overwhelms the brain and interrupts the body’s natural drive to breathe. This also causes oxygen too be cut off from the brain.
According to the U.S. Drug Enforcement Administration (DEA), 6 out of 10 counterfeit pills tested contained a Letha dose of fentanyl.
When prescribed by a doctor, opioid pain relievers are generally safe when taken for a short time and as long was directions are followed. However, they have a high potential for misuse as the medication is addictive and can produce a “high” people may seek out.


Harm reduction is a set of pratical strategies aimed at reducing negative consequences with drug use. It's putting protectove measures in place to prevent a negative outcome such as injury or overdose.
We are constantly using harm reduction strategies in our lives, many have become habits we don’t even think about such as…
Using sunscreen is a harm reduction strategy by protecting your skin, the largest organ in your body, from UV damage.
Using sunscreen is a harm reduction strategy by protecting your skin, the largest organ in your body, from UV damage.
Using sunscreen is a harm reduction strategy by protecting your skin, the largest organ in your body, from UV damage.
Using sunscreen is a harm reduction strategy by protecting your skin, the largest organ in your body, from UV damage.
Using sunscreen is a harm reduction strategy by protecting your skin, the largest organ in your body, from UV damage.
All of these are examples of things we do to protect ourselves and others from a negative outcome.